Search engine optimization (SEO) is a vital aspect of digital marketing, influencing website visibility and organic traffic. In the realm of SEO, two techniques often employed to address content duplication issues are canonical tags and redirects.
Initially, if you see, you might think that both are the same. But actually, they are not the same, and they have different purposes for use.
This blog delves into the comparison between these methods, focusing on the effectiveness of canonical tags for optimizing search engine rankings. By examining the functionalities, benefits, and considerations of canonical tags, I aim to provide insights for making informed decisions in your SEO strategy.
Let’s explore the world of canonical tags vs redirects and determine their impact on SEO.
Understanding Canonical Tags
Canonical Tag is an HTML format code that passes the signal to the search engines or Google if any duplicate or master copy of the webpage.
Example:
- Page 1: https://example.com/main-page
- Page 2: https://example.com/duplicate-page
Your website has two pages with the same content, and according to the webmaster guidelines, you are not allowed to index both pages with the same content.
You must clarify that Google or search engines should provide the rank on one page instead of both.
I hope you know about canonical tags and that you can use them like a pro by reading my ultimate guide to using them.
Exploring Redirects
Redirects are a fundamental aspect of web development and SEO strategy. They are techniques used to redirect website visitors from one URL to another.
When a redirect is implemented, it automatically sends users and search engines to a different URL than the one they originally requested.
Example:
Here are two URLs:;
- https://example.com/contact/
- https://example.com/contact-us/
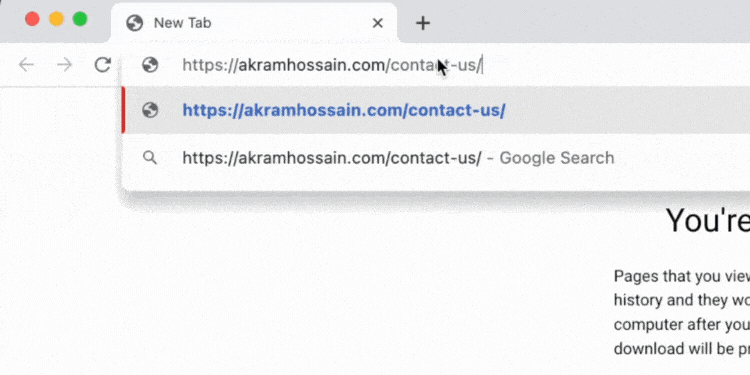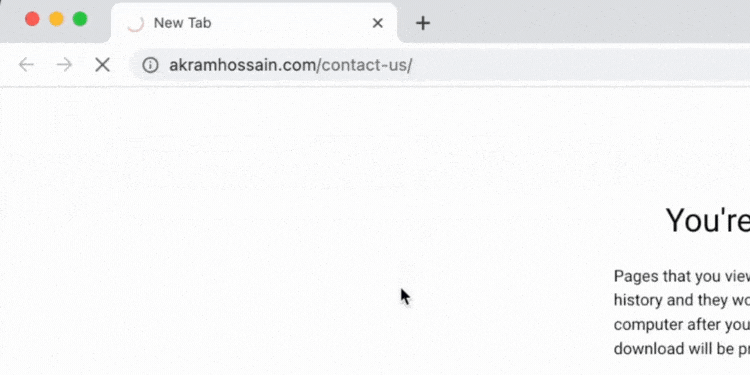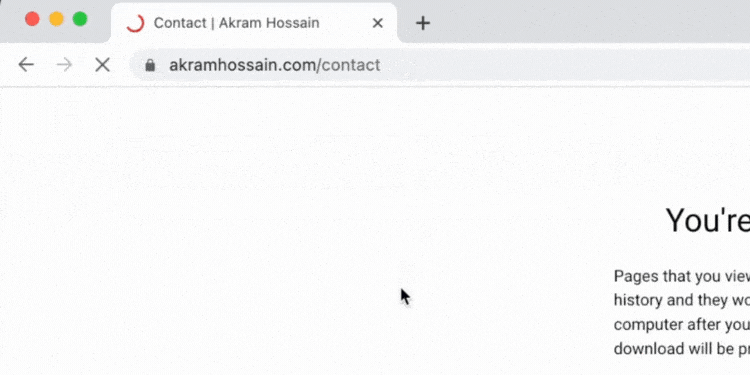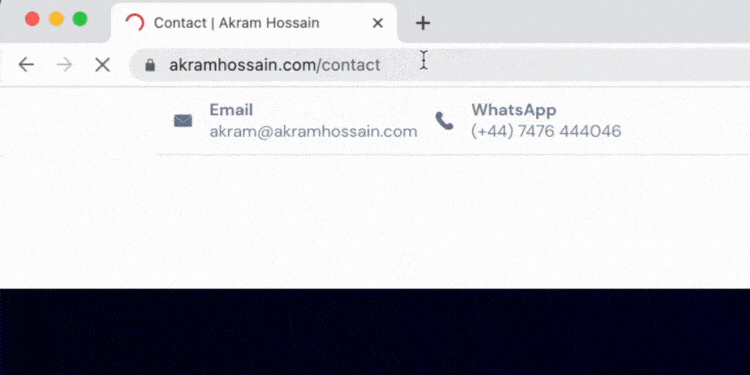
As I redirect /contact-us/ to /contact/, users and search engines will automatically visit /contact/even if they want to visit /contact-us/ page.
Note: Redirect is only being used when the page has been broken, or you don’t want to visit someone that page.
Purpose of Redirects:
Redirects serve several essential purposes in web development and SEO, including:
a. Website Restructuring:
When redesigning or restructuring a website, redirects ensure a seamless transition from old URLs to new ones. This helps preserve search engine rankings, inbound links, and user experience.
b. Content Consolidation:
Redirects are employed when consolidating similar or duplicate content into a single URL. By redirecting multiple URLs to a canonical URL, the consolidated content receives proper indexing and avoids diluting search engine rankings.
But most of the time, Canonical Tag should be used here instead of redirection because it might be important to both pages’ content.
c. URL Changes:
Redirects are crucial when changing a URL, such as updating page slugs, modifying directory structures, or implementing URL optimizations.
Redirects ensure that users and search engines can access the content via the new URL without encountering broken links.
d. Error Handling:
Redirects can handle and redirect users from error pages like 404 Not Found errors or other server response errors to relevant and functional pages. This improves user experience and helps retain visitors to the website.
e. Mobile and Responsive Websites:
Redirects play a role in redirecting mobile users to a mobile-friendly version of a website or responsive web design. By automatically detecting the user’s device and redirecting them to an optimized version, the user experience is enhanced.
You should not randomly delete and redirect to a new page or home page; it may harm your rank.
Let’s clarify with an example;
Assuming you have a URL that contains https://example.com/best-seo-tools/, and you have just removed it.
You should redirect it to the Home Page because Google already considers that URL as the Best SEO Tool, and your home page doesn’t contain that particular content as expected by Google.
What is the solution here? Simple: remove this URL’s cache from Google Search Console “URL Removal” and wait for the confirmation for clearing.
Not every broken link needs to be redirected or replaced by another URL; if you have a similar kind of page on your site, then use a redirect.
Types of Redirect:
If you use any WordPress plugin like RankMath or Yoast SEO. Then, you will see different types of redirections;
301 Permanent Move: When the page does not completely exist, and you want to pass visitors to another page. You can use this type.
Another interesting thing you should know is that 301 redirect works if you remove redirect after 1 year. Ahrefs has tested it and published a complete article on it.
302 Temporary Move: When you think you should update the current page, you won’t want to share this page during the page.
You can use this type while updating the page, and your visitors will be redirected to your preferred page.
307 Temporary Redirect: Use this type when your URL gets lost temporarily. You just have to replace this URL with a new one.
A 307 redirect is intended for temporary situations. It informs search engines that the original URL will be accessible again in the future, so they should continue to index and crawl it.
Canonical Tags vs Redirects: When Should Use?
With the above discussion, you should know the difference between Canonical Tags and Redirects.
Now, let’s move on to the topic;
When should you use Canonical Tag?
You have two or multiple pages, and you have to keep these pages for different purposes. Obeying the webmaster guidelines, you can’t offer search engines to rank all pages.
In this case, you have to use the canonical tag. Google or search engines will understand the purpose of all pages and consider one page for originality.
Conditions: If your website needs to keep the same content on duplicate pages, you should use a Canonical Tag to indicate originality.
It will help you to prevent penalization from search engine guidelines.
So, one thing is clear: When you have to keep multiple pages on your site, you have to use Canonical Tag.
When should you use Redirect?
Basically and technically, redirects should be used for broken and missing purposes. When we get errors like 404, you know why that link is missing or does not exist.
In that case, redirects help to send traffic and the search engine’s bot to another live page.
Look, here, we only use redirect when we have only one live page. Instead, Canonical is used for multiple live chats and ensures originality.
- Redirect doesn’t prove any originality or master copy of any page; it just passes the visitors and search engines to another URL.
- Canonical passes the search engines to the original or master copy of the duplicate pages and redirects both visitors and search engines.
Final Verdict
Look, Canonical tags vs. redirects are a very important topic that we should know, and we should implement these two things very sensitively.
You should not use them randomly without thinking about their point of usage. With Canonical Tag, you can define the master copy of your content that gives transparency and clarity to the search engines.
Besides, Redirects helps you to move the users and Google or search engines from a broken or damaged URL to another perfect and managed page URL.
According to Google’s webmaster guidelines, broken links and duplicate content harm your ranking and indexability.
To manage broken links, you should use redirects, and to manage duplicate pages, you should use Canonical Tags.
Both are important for SEO; depending on the purpose and usage, you can’t ignore one rather than the other.
So, decide upon the website’s situation and identify the better option to use.
You already know the usage and benefits of them. So keep working and boost your SEO potential.